- 09/24/2021
The Galileo constellation is the new North Star
Like stars, the Galileo constellation seeks to provide precise positioning and timing services to the users.
The North Star (Polaris) has helped navigation for centuries. Like stars, the Galileo constellation is a set of navigation satellites orbiting the Earth with the objective to provide precise positioning and timing services to the users.
Since ancient times humans have been fascinated by stars in the sky. As science advanced, the study of stars helped people to know where they were. Sea navigation played a key part in the development of location technology.
For centuries, the height of the Sun and Polaris stars was used to calculate the distance from the Equator line (latitude). However, navigators found it very difficult to know how east/west (longitude) they were from the moment they started the route. They made estimations of the traveled distance towards east or west based on the time and speed of the vessel. Inaccuracy in either time or speed measurement led to large errors in the computation of longitude.
The first sea voyagers soon realized they needed portable navigation tools to avoid deviations in the routes. The sextant was one of the first human-made tools that helped with the calculation of latitude, while the computation of longitude still remained a challenge. It was key to accurately measure the time and the speed of the vessel to compute the travelled distance. Accurate chronometers were used by sailors until universal radio signals appeared. The evolution of technology during the 20th century led to the development of instruments, which improved sailors experience and safety.
Unlike Polaris, Galileo was not created in the big bang at the beginning of the universe and it is not a group of stars. Galileo is a constellation of navigation satellites and it is the result of the knowledge and joint effort of European engineering teams.
The first experimental Galileo satellites were launched in December 2005 with the purpose of testing system technologies in orbit. 10 years ago, on 11 October, the first two operational Galileo satellites were launched, and the first position fix with Galileo satellites was achieved in March 2013.
Satellite positioning has become an essential service that we often take for granted. After the addition of Galileo, the European Global Navigation Satellite System, to the global GNSS services in December 2016, users benefit from a more reliable, robust and accurate positioning. Europe’s research and development, and sectors across many industries, leverage Galileo’s increased accuracy in countless products and services, creating added value for the European economy and improving the lives of citizens.
The performance of Galileo has been gradually improving as additional satellites have been added to the constellation. Users can now benefit from its full first-class performance, reliability and coverage. The European GNSS Service Centre (GSC) has a dedicated Satellite Launch Information Page for all the information regarding Galileo launches.

How the Galileo constellation evolved along the years.
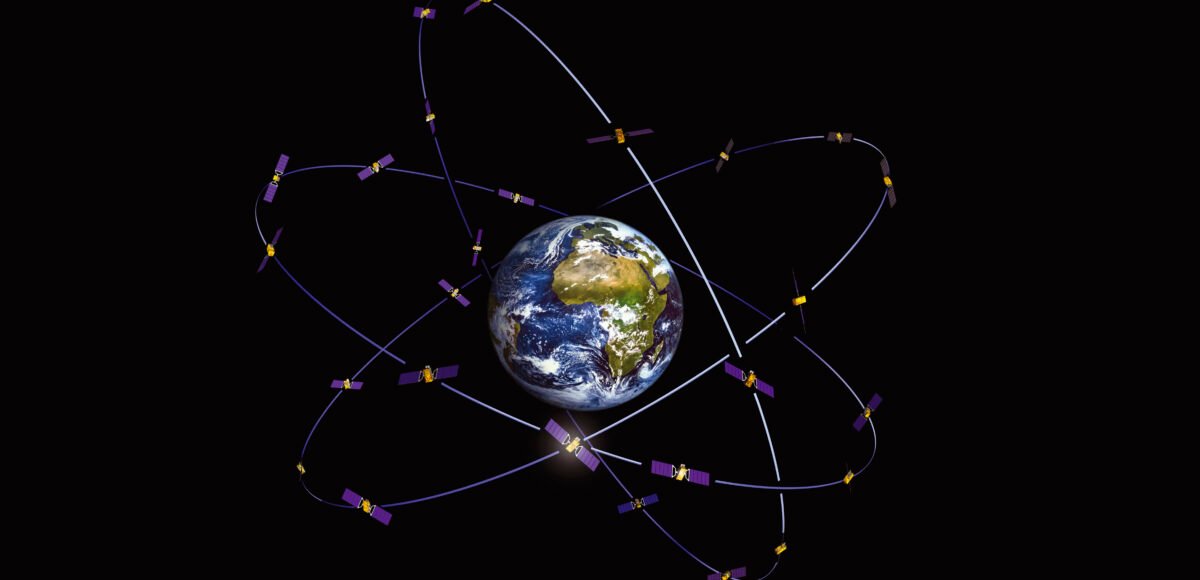
How do Galileo satellites provide global coverage? The satellites orbit the Earth at an altitude of 23 222 km. Galileo has been designed following a type of constellation known as Walker 24/3/1. The constellation consists of 24 satellites homogenously distributed in three orbital planes with an inclination with respect to the Equator line of 56 °. The Galileo satellites orbit the Earth to provide submeter-level positioning and timing services accurate in the order of one-thousandth of one-millionth of a second.

Galileo Constellation Walker 24/3/1 represented based on the Earth-centred Inertial (ECI) coordinate frame.
More detailed information on the orbital parameters of each Galileo satellite can be found in the Orbital and Technical Parameters Page.
The current status of Galileo and all updates are published on the GSC’s Constellation Information page. All satellite status changes are communicated through the Notice Advisory to Galileo Users (NAGU). The constellation information table publishes the active NAGUs which apply to each satellite at that moment. You can subscribe to the Galileo NAGUs notifications by selecting it on the “Subscriptions” tab in the user area.
For more information, visit the GSC Website where you can access to the Helpdesk and find essential Galileo documentation, such as the Open Service Definition Document (SDD), and many other Galileo system and services information.



